
Jaw available individually as well, please inquire. Skull: compared with the earlier species, Australopithecus afarensis, the skull showed some slightly more human-like features such as a smaller brow ridge and a slightly arched (rather than flat) forehead area. Previously, only fragments had been found of Australopithecus anamensis, the oldest. Image: Pavel vejnar/Wikicommons Three and a half million years ago was the heyday of Australopithecus afarensis. Some are reconstructions made by anthropology professionals using fragmentary elements from original discoveries and extrapolating the missing parts from those (i.e. A rare 3.8 million year-old skull found in Ethiopia is rewriting our understanding of the human family tree. The skull, referred to as MRD, represents the early human ancestor known as Australopithecus anamensis that lived between 3.9 and 4.2 million years ago. OctoThe 3.5-million-year-old skull of Kenyanthropus platyops.

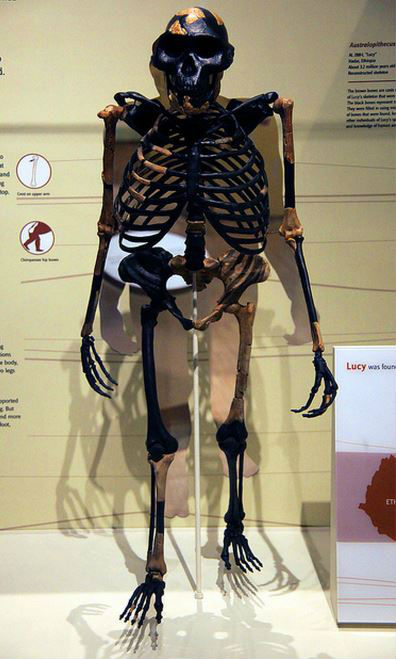
The majority of the casts in this line have been recreated by our team of anatomical sculptors. The Bone Clones® Fossil Hominid line is composed of discoveries from anatomically modern humans, archaic humans, early Homo, early hominins, and other hominids. It is a generalized representation of a male afarensis-not reflective of any one specimen. This full-size skull was sculpted for Bone Clones by scientific sculptor Steven Wagner. Like humans, they had small canine teeth and had a lower body capable of bipedal walking. Like apes, australopithecines had long arms with curved fingers, a flat nose and strong jaw with a cranial capacity ranging from 375 to 500cc.

They had ape-like and human-like characteristics. The 2.5-million-year-old skull was darkened by manganese. The australopithecines are only known from Africa none have ever been found in Europe or Asia. Paleoanthropologists Alan Walker and Richard Leakey unearthed the Black Skull ( KNM-WT 17000) in 1985 at the site of West Turkana, Kenya. From then until 1960 almost all that was known about australopiths came from limestone caves in South Africa. He called it Australopithecus africanus, meaning southern ape of Africa. Australopithecus afarensis is the best represented early hominid with approximately 300 individuals representing the species. In 1925 South African anthropologist Raymond Dart coined the genus name Australopithecus to identify a child’s skull recovered from mining operations at Taung in South Africa.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
